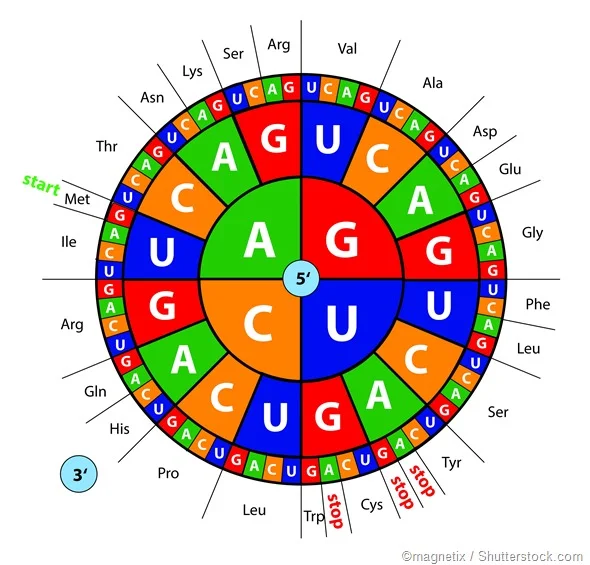
Codons refer to 64 distinct sequences of three consecutive nucleotides in DNA. These sequences play a crucial role in either providing instructions for the synthesis of specific amino acids or serving as termination signals to conclude the process of translation, which is essential for protein synthesis. Codons consist of various triplet combinations of the four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), or uracil (U). Among the 64 potential codon sequences, 61 encode the 20 amino acids responsible for protein formation, while the remaining three function as stop signals.
An illustration of a codon is the sequence AUG, which dictates the amino acid methionine. This AUG codon not only directs the synthesis of methionine but is also present at the commencement of each messenger RNA (mRNA), signifying the initiation of protein formation. Notably, methionine and tryptophan are unique among amino acids as they are exclusively encoded by a single codon each (AUG and UGG, respectively). Conversely, the remaining 18 amino acids rely on two to six codons for their coding. The genetic code is deemed degenerate because most amino acids share multiple codons. Interestingly, the same codons are responsible for specifying identical amino acids across nearly all species.
Despite the vast diversity of life on Earth, the genetic code is remarkably conserved across species. The same codons uniformly dictate the synthesis of identical amino acids, underscoring the universal language embedded within the DNA script. This universal code acts as a testament to the shared ancestry and interconnectedness of all living organisms.
I can never imagine how cool it would have been to be one of the people who discovered the basic molecular code of life, but I am happy to share some basic information regarding it with you guys. Thank you guys for reading this blog and I'll see you in the next one!.
References:
Comments